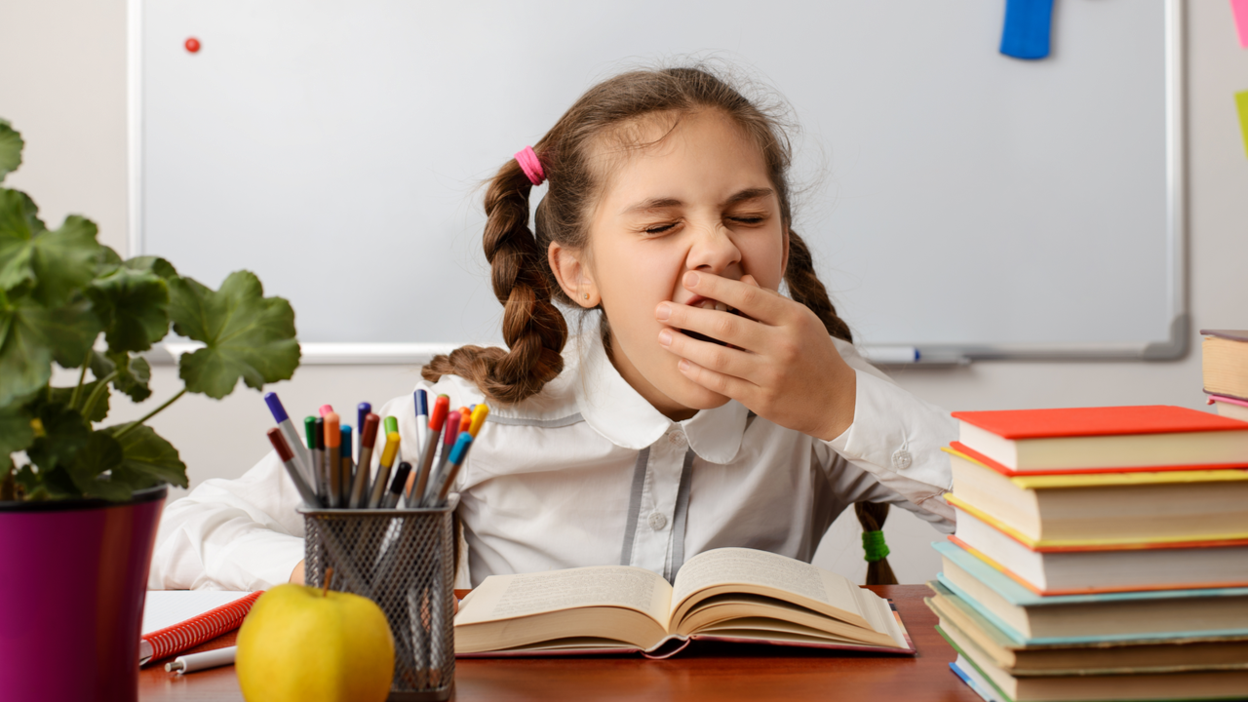
Adequate sleep is an important part of a healthy lifestyle, especially in children. Several studies in the past have highlighted the important role of sleep plays in children’s development. However, inadequate sleep can also hinder brain functioning in children, particularly pre-teens, according to researchers at the Children’s Hospital in Boston, United States.
In a paper published in the journal Cerebral Cortex Communications, the researchers have revealed that inadequate sleep can hinder brain organization in early adolescents.
"Preteens' brain circuits are rapidly maturing, particularly those supporting higher-level thought processes like decision-making, problem-solving, and the ability to process and integrate information from the outside world,” Caterina Stamoulis, lead author of the paper and director of the Computational Neuroscience Laboratory at Boston Children's Hospital, said in a press release. “We show that inadequate sleep could have enormous implications for cognitive and mental health for individual children and at the population level."
Researchers analysed sleep data and brain imaging data from nearly 5,500 children aged between 9 and 11 years. The sleep data was collected from the children’s parents through surveys on sleep patterns, including duration, latency, wake up times, difficulty in falling asleep. They also recorded data for other difficulties that hindered sleep such as snoring, nightmare, difficulty breathing, sleepiness during the day, and more.
Along with brain imaging data obtained through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the researchers identified multiple neural networks within the brain that are crucial to cognitive functioning. They then examined how these networks coped with different qualities and quantities of sleep.
"The network abnormalities we identified can potentially lead to deficits in multiple cognitive processes, including attention, reward, emotional regulation, memory, and the ability to plan, coordinate, and control actions and behaviours," Stamoulis added.
Furthermore, the researchers found that girls tended to sleep less than boys of the same age, while longer sleep times were associated with higher household incomes. Higher times spent looking at screens along with being overweight also tended to reduce the duration of sleep.
Cover Image: Shutterstock