Does the First Amendment apply to public-access cable?
The Supreme Court asks whether a New York City network is a “state actor”

By S.M. | NEW YORK
FREEDOM OF SPEECH, one of the five rights enshrined in the First Amendment, offers little solace to people silenced by private entities. If an arm of the government is suppressing your speech—on a street corner or in a school, say—you are protected. But a company, club or newspaper unaffiliated with the government has no obligation to let you speak; they can curate ideas within their walls or pages however they like. The line between spaces where free speech is a constitutional right and where it is not is to an extent clearly defined, but there are some venues where an otherwise private entity behaves like a state or acts as an agent of the government. One such arena posed a conundrum for the Supreme Court on February 25th, when the justices heard Manhattan Community Access Corp. v. Halleck.
Discover more

Many Americans can decide their own policies. What will they choose?
Three issues will dominate state ballot measures in November
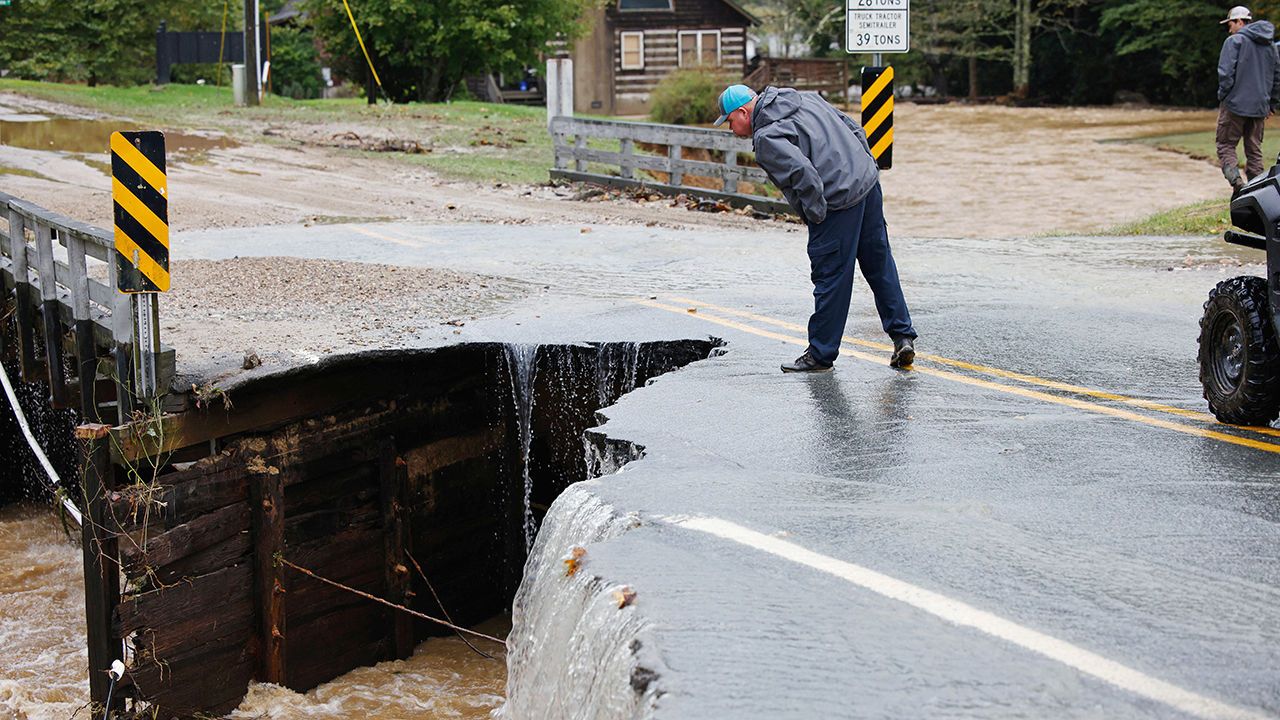

Hurricane Helene was America’s deadliest storm in nearly two decades
It wiped out North Carolina’s mountain towns
Crypto bros v cat ladies: gender and the 2024 election
How the campaigns are exploiting and reshaping the battle of the sexes
A ports strike shows the stranglehold one union has on trade
East coast longshoremen are already among America’s best-paid manual workers
The vice-presidential debate was surprisingly cordial
Its high-minded tone worked to J.D. Vance’s advantage
Tim Walz is the most popular candidate on either ticket
How much difference does that make?