Kirigami computer has high-density memory and doesn't need electricity — researchers demo new mechanical computing design
The Kirigami computer's complexity is so deep that it can replace traditional electronic computers for certain tasks.
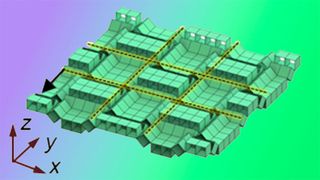
When we think of computers, we almost always think of modern-day computers that run on electricity. But electricity doesn't drive all computers. Instead of using transistors and electricity, North Carolina State University researchers have developed a computer that utilizes the art of Kirigami, which is the art of origami combined with cutting to create and control 3D shapes. The Kirigami computer can be manipulated to represent several states, including 1 and 0, like all computing architectures behind our PCs and phones today. However, the research also proved that cubes could be used to represent 2, 3, or 4 states and to define a 5-state computer.
The Kirigami computer has 64 interconnected cubes measuring just 1 cm in width and height. The cubes are arranged so that their geometry represents data. Manipulating (or editing) data is done by pushing the cubes up or down, which changes the geometry of the connected cubes. The 64-cube computer can be used independently or connected to additional 64-cube Kirigami computers to increase complexity, boosting the system's storage (data) capacity.

As its name suggests, the Kirigami computer was inspired by the Japanese art of the same name. For those unfamiliar with it, Kirigami is a Japanese paper folding art form that allows creators to build 3D paper structures that stick out from the paper they are created with. If you've ever opened a pop-up book or card featuring 3D objects, that is Kirigami.
Each cube is connected to another by thin strips of elastic tape. When users go to edit data, they have to pull on the edges of the cube structure itself, which pulls on the elastic tape and causes them to change each cube position (up or down). Releasing the structure locks the cubes in place — almost like saving a Word doc or locking a file to "read-only" status.
According to Jie Yin, an associate professor at NCSU, the goal of the Kirigami computer is to develop a stable mechanical system for storing data. The primary focus of the Kirigami computer is binary computing functions. However, she says there is potential for more complex computing down the road, with the possibility of the Kirigami computer evolving into a five-state computer that can represent 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 states (not just binary states).
The complexity of the Kirigami computer is virtually endless. Jie Yin talks about the idea of using Kirigami computers to run varying functions that are not related to each other, such as data encryption and haptic communication. For some perspective, Jie Yin says a simple Kirigami metastructure with just nine functional units has more than 362,000 possible configurations. Now, add the computer's full 64 cubes in, and the number of possible configurations increases exponentially.
The best part of the Kirigami computer is that it is claimed to be immune to the vulnerabilities electronic computers are prone to, such as EMPs and remote hacking. It also doesn't utilize any electricity, at least in its current form, which would improve its cost-to-performance ratio and make it virtually maintenance-free. However, how that plays out when integrated into a device remains to be seen. If the Kirigami computer makes it out of the research phase, it could be used to replace modern-day electronic computers for certain tasks, like storing data as a backup machine for governments, banks, and businesses to combat computer viruses, theft, and other security vulnerabilities.
Stay On the Cutting Edge: Get the Tom's Hardware Newsletter
Get Tom's Hardware's best news and in-depth reviews, straight to your inbox.

Aaron Klotz is a contributing writer for Tom’s Hardware, covering news related to computer hardware such as CPUs, and graphics cards.
-
husker After reading this article... so many questions. Is this "computer" made of paper or is that just an analogy. If not, what is it made of? If it is paper, how is that any kind of practical use? Or is it currently just a mathematical theory run in a simulation, with some future material to be determined? The title suggests it's high-density storage, but what is the current storage density and the potential that they see and how does it compare to the terabytes of data that currently fit on a stick of gum? The article mentions configurations of cubes, but how to translate that into current storage density terminology? How would this interface with a conventional computer? I guess it's EMP proof but so were punch cards.Reply -
derekullo "The best part of the Kirigami computer is that it is claimed to be immune to the vulnerabilities electronic computers are prone to, such as EMPs and remote hacking. It also doesn't utilize any electricity, at least in its current form, which would improve its cost-to-performance ratio and make it virtually maintenance-free."Reply
"Each cube is connected to another by thin strips of elastic tape. When users go to edit data, they have to pull on the edges of the cube structure itself, which pulls on the elastic tape and causes them to change each cube position (up or down)."
Nothing says maintenance free like thin strips of elastic tape! -
Notton I assume the next step is to create this from an infinite durability flexible material, rather than tape.Reply
something like the stuff in the below video
97t7Xj_iBv0 -
husker Replybaboma said:>After reading this article... so many questions.
It's an "odd news" piece, which qualifies as a filler article. If you are interested, you can always Google for more detail.
>If it is paper, how is that any kind of practical use?
>"The best part of the Kirigami computer is that it is claimed to be immune..."
It's a weird product, which is the point in itself, not so much its utility. The best part of this "computer" is that it encourages lateral aka out-of-the-box thinking. It promotes creative solutions and fights against groupthink. It's an essential part of learning. If you have kids, you would want them to be exposed to this and other "weird" solutions.
That is a universal good. Practicality is not the point.
I had considered that, but ultimately the article does not support that conclusion. The article never mentions education. Instead, here are some quotes that imply it is, in fact, intended to be taken seriously as a real-world solution:
"According to Jie Yin, an associate professor at NCSU, the goal of the Kirigami computer is to develop a stable mechanical system for storing data.""Jie Yin talks about the idea of using Kirigami computers to run varying functions that are not related to each other, such as data encryption and haptic communication.""The best part of the Kirigami computer is that it is claimed to be immune to the vulnerabilities electronic computers are prone to, such as EMPs and remote hacking.""If the Kirigami computer makes it out of the research phase, it could be used to replace modern-day electronic computers for certain tasks, like storing data as a backup machine for governments, banks, and businesses to combat computer viruses, theft, and other security vulnerabilities."
Most Popular


