Army of the Potomac
Learn about this topic in these articles:
leadership of
- Burnside
- In Ambrose Everett Burnside

…from the command of the Army of the Potomac (Nov. 7, 1862), Burnside (over his own protests) was chosen to replace him. After a crushing defeat at the Battle of Fredericksburg (December), Burnside was replaced by General Joseph Hooker (Jan. 26, 1863). Transferred to Ohio, Burnside helped to crush General…
Read More
- Grant
- In Remembering the American Civil War: Overview

…took personal command of the Army of the Potomac in the east and soon formulated a strategy of attrition based upon the Union’s overwhelming superiority in numbers and supplies. He began to move in May, suffering extremely heavy casualties in the battles of the Wilderness, Spotsylvania, and Cold Harbor, all…
Read More
- Hooker
- In Joseph Hooker

… (1861–65) who successfully reorganized the Army of the Potomac in early 1863 but who thereafter earned a seesaw reputation for defeat and victory in battle.
Read More
- McClellan
- In American Civil War: The war in the East

…he began to mold the Army of the Potomac into a resolute, effective shield and sword of the Union. But personality clashes and unrelenting opposition to McClellan from the Radical Republicans in Congress hampered the sometimes tactless general, who was a Democrat. It took time to drill, discipline, and equip…
Read More - In George B. McClellan

…what was to become the Army of the Potomac. He was charged with the defense of the capital and destruction of the enemy’s forces in northern and eastern Virginia. In November he succeeded General Winfield Scott as general in chief of the army. His organizing abilities and logistical understanding brought…
Read More - In United States: Fighting the Civil War

…job of training the Union’s Army of the Potomac.
Read More
- Meade
- In George G. Meade

…Hooker in command of the Army of the Potomac. Meade repulsed General Robert E. Lee at Gettysburg (July 1–3) with great tactical skill; however, he has been criticized by some for allowing Lee’s army to escape after this decisive victory. Although Meade retained command of the Army of the Potomac…
Read More
role in
- Battle of Fredericksburg
- In Battle of Fredericksburg

…night of December 15 the Army of the Potomac withdrew to its camps at Falmouth. The Union had suffered nearly 13,000 casualties, while the Confederates suffered approximately 5,000.
Read More
- Second Battle of Bull Run
- In Second Battle of Bull Run: The Northern Virginia Campaign
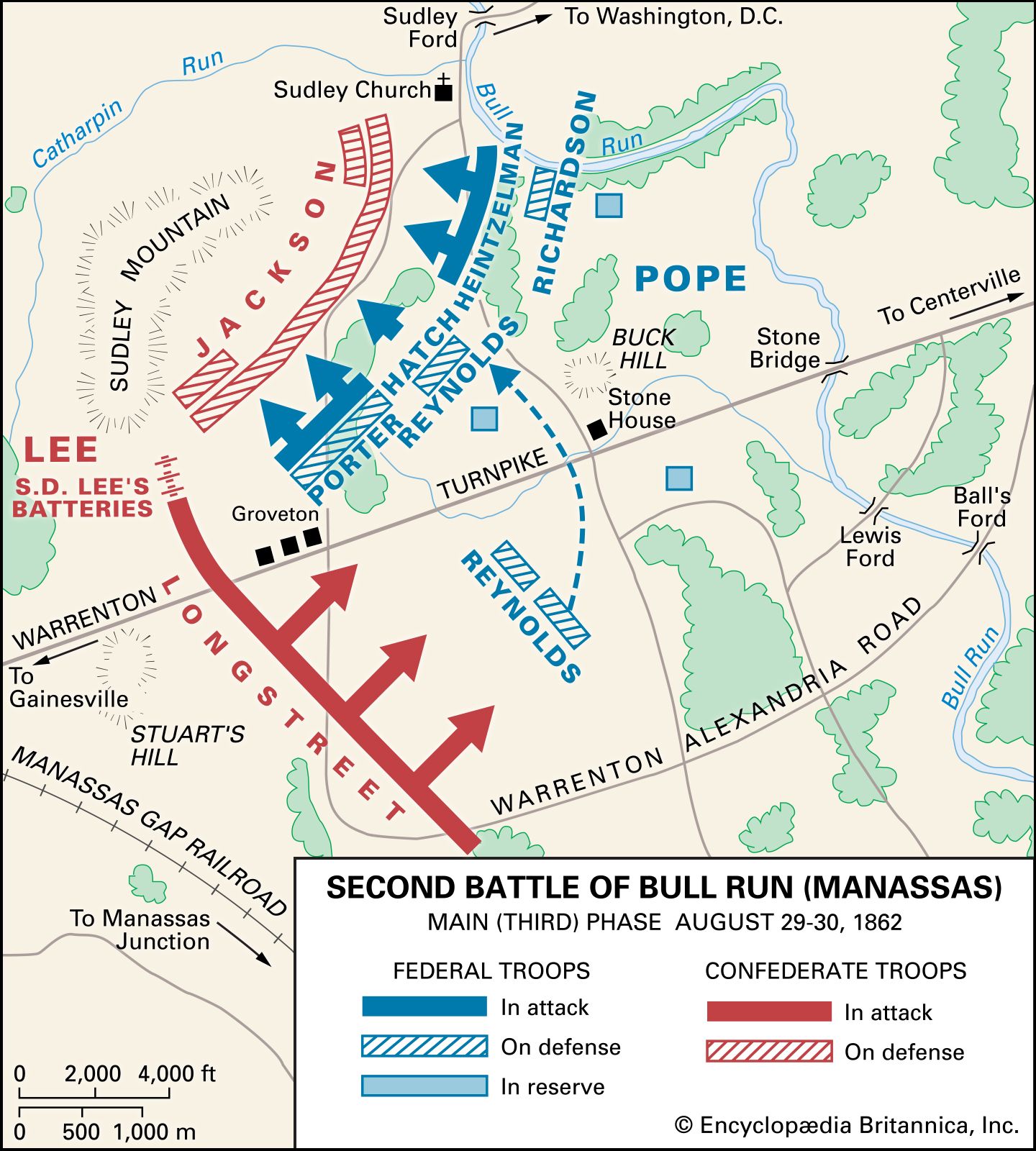
Henry Halleck ordered McClellan’s Army of the Potomac to assist Maj. Gen. John Pope’s newly created Army of Virginia in central Virginia. Until the two Union armies could be combined for a renewed assault upon the Confederate capital of Richmond, it fell upon Pope to defend Washington, D.C., and…
Read More








